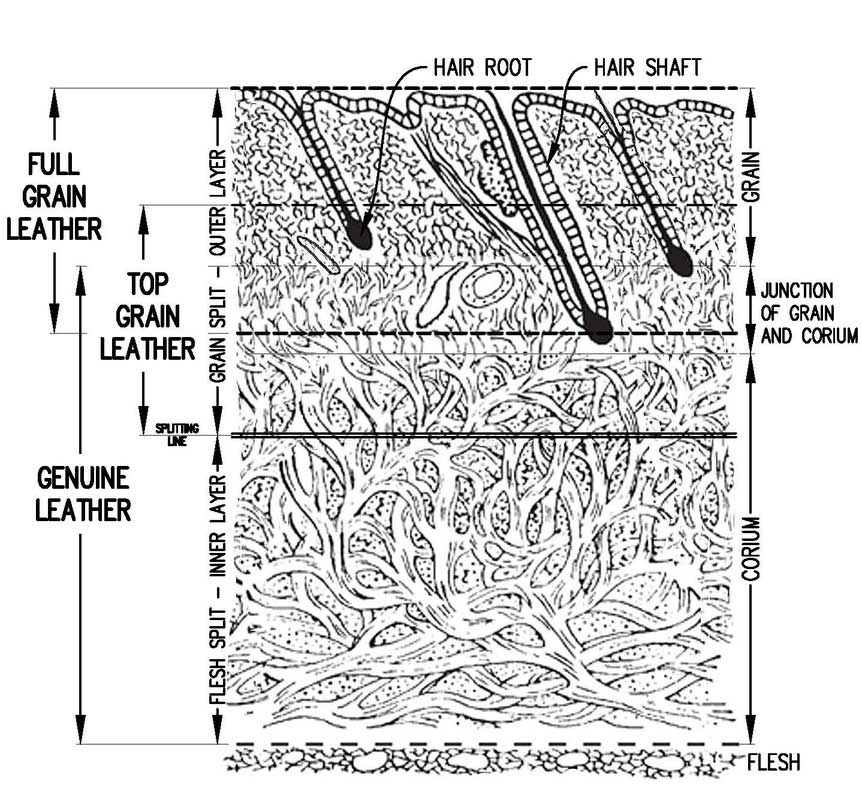
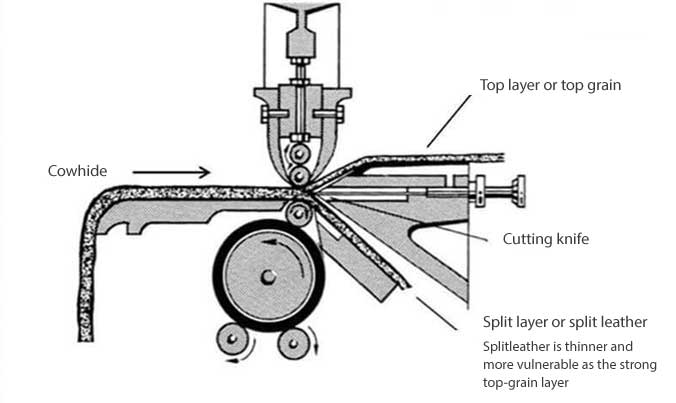
Top-grain leather
This concerns the upper layer of the skin (epidermis) that is split from the lower (split) layer. The top layer is strongest and smoothest layer, so this leather can be applied for many purposes and is often the best suited. The surface may sometimes be slightly sanded or polished to remove any imperfections.
This top-grain leather type of approximately 1.3 to 1.6 mm is made from the most beautiful skins. You will find them on the better seating furniture. Top-grain leather is breathable, strong, maintenance-free and resistant to sunlight.

Full-grain leather
This leather concerns the full skin, not separated into an upper top grain and split layer. The surface of this leather is not sanded or polished to remove imperfections or natural marks from the skin (as opposed to top-grain or corrected leather).
This thick and stiff leather type (full skin) is rarely used for lining seating furniture, rather for bags or belts, etc. Full-grain leather is breathable, very strong, maintenance arm, resistant to sunlight, but also very rough.
Split leather
This is the fibrous, split, bottom of the skin. The coarse fiber is less intensive intertwine than the connective tissue of the upper layer. This makes this leather a bit more weak and a bit more rough. Split Leather is not recomended if you are going to use the chair intense on a daily basis.
PU leather (artificial leather)
PU stands for polyurethane, and is used to produce artificial leather.
Corrected grain
The epidermis has been machined or corrected using an artificial grain below the surface. As a result, natural unevenness becomes less or less noticeable, making this upper layer skin entirely suitable for use. This leather is usually used for the pigmented or coated paint. This type of leather has approximately a thickness of 0.9 to 1.1 mm.
Aniline treatment
Leather with aniline treatment gets an aniline bath that softens the leather. It feels comfortable, soft and flexible.